How hot is the sun?
Life on the Earth was impossible without the Sun and Gases. As the sun is a big ball of gases. Those gases are mostly hydrogen and helium, but the sun also contains small amounts of several other elements, including oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, magnesium, and iron. How hot is the Sun? is the matter of our concern now. The temperature of the Sun varies from 27 million Degrees Fahrenheit (15 million Degrees Celsius) at the core to about 10,000 degrees F at the Surface.
Every 1.5 Millionths of a sec, the sun releases more energy than all human beings. Here we are going to explore how hot each layer of the Sun is.
Source of Heat of Sun
The gaseous plasma mostly having major content of Hydrogen Gas is the construction material of the Sun. NASA claimed in a report that Hydrogen in the Sun core is causing gravitational force within the Sun. This force resulting in high pressure causes a collision of Hydrogen atoms resulting in a new element called Helium. This process is called Nuclear Fusion.
This chain reaction of Nuclear Fusion causes an increase in Energy by increasing 27 mission degrees F. This Energy is then radiated to the Environment through the core of the Sun.
Temperature Zones of Sun
Radiative Zone Temperature
In this Region, Energy is Radiated outward by radiations. The temperature in this region decreases as we move toward the edges.
Convection Zone Temperature
The convective zone is the outermost layer of the Sun’s interior structure. In this zone, energy is released outward by convection, as hot plasma rises and cooler plasma sinks.
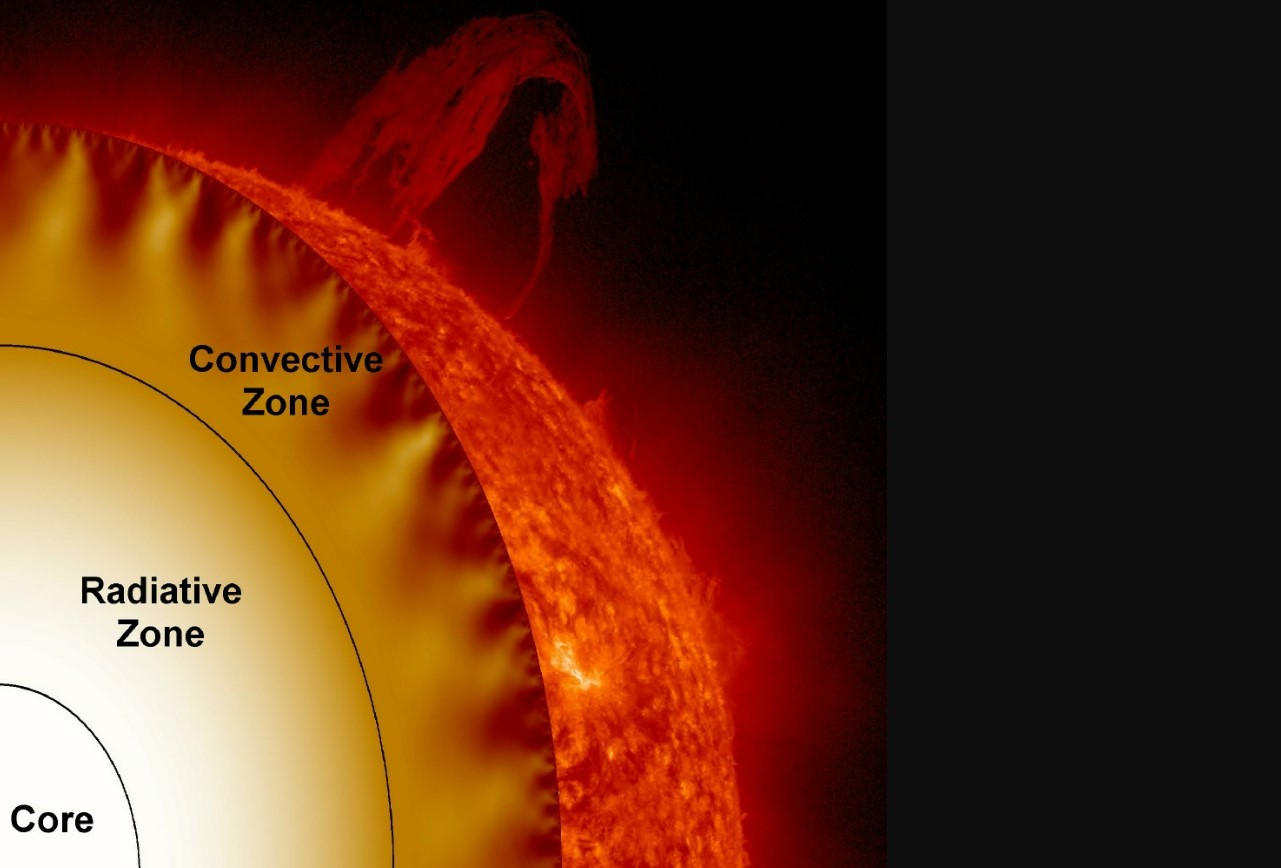
Photosphere
The photosphere is the visible surface of the Sun which we see from the Earth. The temperature in this region is around 5,500 degrees Celsius (9,932 degrees Fahrenheit). This is the temperature at which the Sun’s blackbody radiation peaks and it is what gives the Sun its yellowish-white color.
Comparison of Temperatures in Different Zones
| Zone/Layer | Temp in Degrees Celsius | Temp in Degrees Fahrenheit |
|---|---|---|
| Core | 15,000,000 | 27,000,000 |
| Radiative Zone | 2,000,000 - 7,000,000 | 3,600,000 - 12,600,000 |
| Convective Zone | 2,000,000 - 6,000 | 3,600,000 - 10,800 |
| Photosphere | 5,500 | 9,932 |
Is Sun Causing Forest Fires?
The hot Sun is the primary source of heat and light for habitants of Earth. It certainly plays a role in the occurrence of forest fires.
According to the NFPA or Disaster Management Authorities, it is not the direct cause of such fires. The primary causes of forest fires are common human activities, such as campfires, cigarettes, and even intentional arson.
However, Sun can indirectly contribute to forest fires by drying out vegetation that enhances the chances of getting fires. During hot, dry weather, the Sun’s intense heat can quickly dry out the moisture in leaves, branches, and other organic matter, turning them into kindling that can easily ignite.
Forest Fires and Firefighting Methods
Firefighters play a crucial role in extinguishing these fires and preventing them from spreading further to nearby communities.
- Starvation– Primarily firefighters create fire breaks by removing combustible materials
- Cooling– Use of water or other fire retardant chemicals to extinguish flames
Overall, the key to effective firefighting is a combination of preparation, planning, and rapid response to minimize the damage and bring all of us to the appreciation of firefighters.

Hi, I am John Smit a Captain in Fire Department City of Newyork with over years of experience in the field of Firefighting and HSE. My passion for fire safety started when I was a young boy and witnessed a neighbor’s house go up in flames along with precious lives. Since then, I had dedicated my life to ensuring the safety of buildings, properties, and individuals in case of a fire and medical emergencies.

